Laryngeal papillomatosis
Laryngeal papillomatosis is happened to be as often as laryngeal polyps. They are the result of the proliferous process developing in epithelium and connective elements of mucous membrane under the influence of the Human Papilloma Virus. The isolated papillomas are very rare, in most cases they are the multiple formations, which can proceed not only in larynx, but at the same time on the soft male, palatine tonsils, lips, skin, mucous membrane of trachea. Papillomas anticipate very often, that's why this disease is named papillomatosis. More frequently Papillomas occur in early childhood and very seldom at grown-ups. Some cases of inborn papillomas are described. Structurally, the papillomas represent the formations of two layers: papillary layer consisted of connective tissue and epithelial layer. At multiple children papillomas the connective plentifully vascularized elements are prevailed, as the elements of surface epithelium are prevailed in “older” papillomas of young men and grown-ups. Such papillomas have white and grey colors, in contrast with the first which are pink or red colors. Laryngeal papillomatosis epidemiologyAccording to different authors, the papillomas make 15,9-57,5% in the structure of benign tumors. The disease can begin both in children's age and in adulthood. The juvenile papillomatosis is more often occured (in 87%), the symptoms of which are revealed in the first five years of life. Prevention of laryngeal papillomatosisPreventive events come down to dynamic surveillance over the patient, adherence the gentle voice mode by the patient, elimination of a professional harmfulness, treatment of a gastrointestinal tract concomitant pathology (reflux esophagitis) and respiratory tracts, inflammatory diseases of an ear, a throat and a nose, prevention of HPV infection. CauseThe infection with the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Respiratory or laryngeal papillomatosis is basically caused (in 80-100% cases) by papillomaviruses by 11 (rare by 6) type. These are the viruses with oncogenic DNA, stimulating the proliferation of epithelial cells in the basal layer of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract with the formation of papillomatous growths. ClassificationThere are two types of papillomatosis according to age, severity of clinical manifestations and sources of infection:
The prevalence: 1. limited 2. common 3. occlusive Ways of infection
The pathogenesis of laryngeal papillomatosisThe disease is characterized by rapid course, a tendency to relapse is often accompanied by stenosis of the larynx lumen. The papilloma develops at the adult age of 20-30, or at the old age. The frequent relapses are forced to the numerous surgical interventions, therefore the cicatricial deformations of the larynx are developed among most patients, sometimes leading to the stricture and deterioration of voice function. Bronchial pneumonia may develop among the children, moreover the spread of papillomas in the trachea is diagnosed in 17-26%, in the bronchi and lungs - in 5% of cases. The last one is considered a poor prognostic sign concerning the malignancy. The symptoms of laryngeal papillomatosis
The main clinical sign of the laryngeal papillomatosis is hoarseness and breathing disorders. The severity of the disease is caused with frequent relapses, which can lead to stenosis of the larynx, the possibility of papillomas spread into trachea and bronchi with subsequent development of pulmonary insufficiency and malignancy. The symptoms of laryngeal papillomatosis are determined by the patient's age, localization and incidence of tumors. Common diffuse forms are mostly observed in small children, whereas older children have papillomas with a more limited localization (circumscripta papillomatosis). Adults have more common papillomas on vocal folds, characterized by hyperkeratosis. The main symptom among children and adults is increasing hoarseness, reaching full aphonia. At the same time children have increasing phenomena respiratory disorders, shortness of breath during phisical exercises and other signs of hypoxia. The signs of dyspnoea increase, the spasms of the larynx, stridor and symptoms of suffocation appear. It can lead to child's death, if emergency measures are not accepted. In some cases, the attacks of asphyxia suddenly arise during the trivial intercurrent inflammatory disease of the larynx, developing with its concomitant swelling. The younger the child, the more dangerous these attacks, because of the significant development of the loose connective tissue in the subglottic place, the small size of the respiratory tract and at young children, papillomatosis diffuses and evolves very quickly. All these risky factors of asphyxia should be considered at monitoring these children. Asthma is not observed at adults, and the only symptom indicating a substantial formation in the area of the glottis is hoarseness. Diagnosis of laryngeal papillomatosis
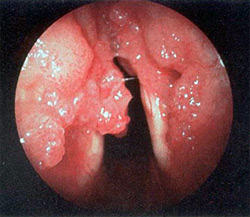
Differential diagnosticsIn case of microlaryngoscopy the picture of papillomatosis is very specific — the growth has the view of limited, often multiple papillary excrescences with fine-grain surface and in appearance it resembles a mulberry berry. Its color is dependent on the availability of vessels, the thickness and keratinization of the epithelium, so papilloma can change its color at different periods of the development from red, pale pink to white. The differential diagnosistics is carried out with tuberculosis and larynx cancer. The signs of malignancy are: ulceration of papillomas, the change of vascular pattern, a sharp restriction of vocal folds mobility in the absence of the scar process, submerged growth, keratosis. Difficulties of differential diagnosistics in papillomavirus present have elderly patients and patients with a large number of surgical interventions in their history. The final diagnosis is established by histological examination. Treatment of laryngeal papillomatosisThe aims of treatment
MedicationDuring recent years the doctors often turn to non-surgical medical treatment of papillomatosis in children. The use of modern drugs allows significantly to lengthen the intervals between operations, and in some cases even refuse surgical intervention. Moreover, the most aggressive forms of papillomatosis are best amenable to the drug therapy, which are poorly treated surgically. Such successes became possible when the causative agent had been identified - the human papilloma virus, in particularly its certain types: 6 and 11 types. They also apply the drugs which slow the cells reproduction - cytostatic agents. As they are superpotent substances (they are used in oncology) to treat laryngeal papillomatosis at children, they are used only topically: swab the surface of the vocal folds after the papillomas removal or instead of surgical treatment. A new group of drugs, so-called cytokine therapy, is more and more widely used during last years. Among the drugs of this group for the treatment of respiratory papillomatosis roncoleukin is applied. Antibiotics play an important part in the treatment of postoperative laryngitis, local and general anti-inflammatory therapy. They accept the local application of cytostatics, antiviral drugs and drugs which affect the level of estrogen metabolites and etc. On the base of the immune status study they hold the immune correction. Surgical treatment of Laryngeal papillomatosisTo remove papillomas is used:
But during the operation only the papillomavirus is deleted, the virus itself remains in the body. An effect in the laryngeal papillomatosis treatment is possible to obtain only by a reasonable combination of different methods. If we do only a surgical removal of papillomas without antiviral therapy, the possibility to keep a more or less good larynx, alas, is probably unlikely. Unfortunately, the most common way to help the child at papillomatosis is currently just surgical. The method is extremely simple: to remove papillomatous growths, and thus to create conditions for optimal breathing. It is clear that the surgical intervention has no therapeutic effects on the development of the disease. Therefore it is no surprise that children have several surgeries to remove the laryngeal papilloma: they can have five, ten, and even more than two dozen! Besides, the surgical treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis in children is always associated with additional tissues trauma and leads to two equally unpleasant results: first, frequently the operation increases the growth of new papillomas, and secondly, it always causes the formation of scar tissue, which further degrades the voice and breath. So if it is possible, doctors try to use more gentle methods of treatment of Laryngeal papillomatosis. For example, a laser surgery that much less damages the larynx. An effective method of photodynamic therapy has been developed, when the special substance is administered endovenously - a photosensitiser, then the surface of papillomatous changed parts of the larynx are illuminated with the light of a certain frequency. These methods are used in the clinic of ENT diseases of St. Petersburg medical University named after academician I. P. Pavlov. PredictionThe prediction is usually favorable with combination therapy. |
|
| Homepage | Feedback | Site Map | Job Vacancies | Contacts
© 2004—2020 Brand-Pharm Ltd. All information contained on this website is intended only for medical specialists and cannot be used by visitors for self-diagnosis and treatment. Consult your physician, do not start self-medication!
The website creation and promotion: Alisa Design |



 Laryngeal papillomatosis (papilloma) is a benign neoplasm, formativing from pavement or transitional epithelium and overhanging its surface as a papilla.Papillomatosis is a pathologic process, which is characterized by formation of multiple papillomas on any part of the skin or mucous membrane.
Laryngeal papillomatosis (papilloma) is a benign neoplasm, formativing from pavement or transitional epithelium and overhanging its surface as a papilla.Papillomatosis is a pathologic process, which is characterized by formation of multiple papillomas on any part of the skin or mucous membrane.